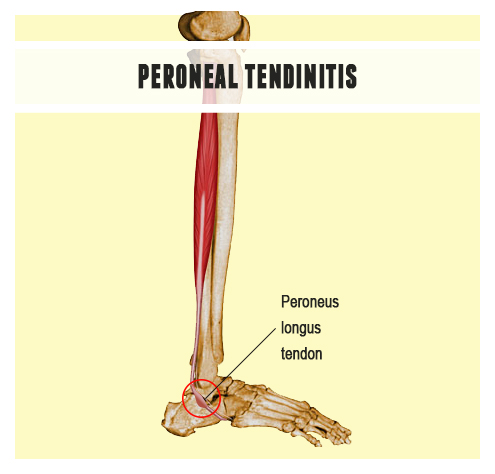
Peroneal tendonitis (also spelled tendinitis) is theinflammation and irritation of one or both of the peroneal tendons. Like all forms of tendonitis, peroneal tendonitis is a condition that may flare up and subside over a period of time. Fortunately, tendintis can be treated with cold compression and blood flow stimulation therapies.
Peroneal tendinitis is usually caused byrepetitive use of the tendons, but can also becaused by trauma such as a rolled or sprained ankle. Little tears in the peroneus longus tendon and the peroneus brevis tendon irritate the tendon fibers resulting in pain and inflammation.
Peroneal tenosynovitis is swelling and inflammation of the peroneal tendons’ sheaths (or coverings) which prevents them from gliding smoothly within the shealths causing pain. Tenosynovitis can occur along with tendonitis and has similar symptoms. It often results in trouble moving the ankle and will feel sore to the touch. In rare cases, tenosynovitis can be caused by infection, so it is always recommended to check with your doctor to rule this out as a cause.
The peroneus longus tendon and the peroneus brevis tendon are two major tendons that run along the outside of your ankle. They are collectively called the peroneal (or peroneus) tendons. These tendons are important becausethey prevent the foot from rolling and causing a lateral (inversion) ankle sprain. The peroneus tendons are slightly weaker than the muscles and tendons on the inside of the ankle and are more prone to tendintis, tears or strains. The tendons can also pop out of the supporting ligaments that hold them in place (a dislocation).
Peroneal Tear and Dislocation
Tearing or dislocation can occur in one or both of these tendons at a time. This leads to pain, swelling, sensitivity and a sense of instability on the outside of the ankle. If you experience a tear or dislocation you should see a doctor as recurrent tearing or dislocation is probably without immediate attention and repair. Stitching and at the worst, tendon replacement may be required for patients suffering from torn or dislocated peroneal tendon(s).
Who is at Risk?
- People who play sports or do activities that involve repetitive ankle movements.
- People who participate in activities such asrunning on uneven surfaces, racket sports, basketball, hiking, or skiing.
- People with high arches in their foot.
- People in aging populations, because our tendons lose elasticity and become brittle.
Symptoms
- Pain and/or swelling along the tendon and possibly up the leg along the fibularis longus muscle during or after activity.
- A burning sensation along the tendon.
- Pain either first thing in the morning or at night.
- Stiffness in the foot and trouble stretching the area.
Ankle Tendon Treatments
Allowing your ankle to rest is always recommended when you are suffering from tendinitis, tendon tear or bone dislocation. Avoid all activities that may have caused the injury or irritation and begin cold compression treatments as soon as possible. The peroneal and posterior tibial tendons are difficult to rest completely as they are essential tendons for walking and daily activities. During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort in your ankle until the pain and inflammation settle.
The trick with healing an ankle tendon injury is getting it to heal with minimal scar tissueformation. Even with optimum healing, there is always less elasticity in previously injured peroneal tendons. This will cause the tendons to hurt during daily activities and exercise. However, if you heal your ankle tendons efficiently and quickly, your chance of re-injury later on is much lower than average.
Fortunately, there are healing tools that can help treat your peroneal and posterior tibial tendons and speed up the healing process so you can get back to a life without pain and risk of further injury. Blood Flow Stimulation Therapy™ (BFST®) promotes blood flow to heal your tendons faster and more completely than any other methods available.